
Materials List – Upstream
INHIBITOR / SCAVENGER
- Corrosion Inhibitor
- Scale Inhibitors
- Corrosion / Scale Inhibitor Combination
- Mud Corrosion Inhibitor
- Brine Corrosion Inhibitor
- Shale Inhibitor
- Hydrate Inhibitor
- Iron Sulfide Inhibitor
- H2S Scavenger
- O2 Scavenger
Completion Fluids & Workover
- Calcium Bromide
- Zinc Bromide
- Calcium Chloride
Alkalinity & pH Control
- Buffering Additive
- Citric Acid
- HF Acid
- Magnesium Oxide
- Potassium Silicate
- Soda Ash
- Sodium Bicarbonate
Weighting & Viscosifiers Agent
- Barite
- Calcium Carbonate
- CMC
- Gelling Agent
- Acid Gelling Agent
- Guar Gum
- Xanthan Gum
- PAC
- Polymeric Viscosifiers
Foam & Anti-Foam Agent
- Defoamer
- Defoamer Silicon
- Foam Agent
- Acid Foamers
Drag & Friction Reducer
- Lubricants
- Cross Linker
- DRA
- Friction Reducer
- Anionic Friction Reducer
- Cationic Friction Reducer
Cleaning Agent
- Acetic Acid
- Anti-Sludge Agent
- Benzoic Acid
- Xylene
- Asphaltene Deposit Treatment Chemicals
- Paraffin Deposit Treatment Chemicals
Salt
- Calcium Nitrate
- Potassium Chloride
- Sodium Sulfite
Drilling & Mud Additive
- Clay Stabilizer
- Drilling Detergent
- HCl
- Iron Control Agent
- Fluid Loss Additives
- Coagulating Agents
- Silt Suspended
- Spotting Fluids
- Fluid Loss Pills
- Spacer Polymeric Materials
- Bentonite
Emulsifiers & Surfactant
- Primary Emulsifiers
- Secondary Emulsifiers
- De-Emulsifier
- SDVES
- Surfactant
Cementing Specialty Chemicals
- Retards
- Cement preflush
- Expansion Additives
- Gas Block Additives
- Gas Migration Additives
Anti-Sludge
Oil sludge is a complex emulsion of various hydrocarbons, water, heavy metals and solid particles. The main source of the production of sludge are resin, paraffin, asphalt and hydrocarbons with various molecular weight in crude oil. Each of these factors causes the formation of sediment and sludge due to a different reaction with acid.
Anti-Sludge using to prevent the destructive effects of oil sludge. This agent can be substance as cationic surfactant, Dodecyl benzene, sulfonic acid, corrosion inhibitor, reducing iron agent or other additives. Other applications of this materials are:
- increasing the withdrawal of crude oil and gas resources
- Solution of mineral materials such as CaCO3, MgCO3
Bentonite
The Bentonite was first used by Knight in 1898. This term is derived from the local term “Benton Shale” in the states of Wyoming, USA. Bentonite is a mineral clay that is essentially composed of Smectite group minerals. Smectite consists of diacethorodic and tri-octahedral series. One of the most important uses of bentonite in the drilling industry. A material composed of clay minerals, predominantly montmorillonite with minor amounts of other smectite group minerals, commonly used in drilling mud.
Bentonite swells considerably when exposed to water, making it ideal for protecting formations from invasion by drilling fluids. Montmorillonite forms when basic rocks such as volcanic ash in marine basins are altered.
A clay mineral that is composed principally of three-layer clays, such as montmorillonite, and widely used as a mud additive for viscosity and filtration control. Commercial bentonite ores vary widely in amount and quality of the swelling clay, sodium montmorillonite. Bentonite forms 5-2 wt% uses for mud additives based water.
Sodium bentonite is used in drilling oil and gas. The relatively large sodium bentonite shells are converted to colloidal particles by freeing in water and release the electrical energy stored in the crystalline network, and swell about 15 to 30 times the initial volume.
This property is used in drilling to disassemble heavy materials and cut off drilling. Bentonite thus creates a coating on the wall of the well and prevents the migration of oil and gas and makes the wall stable and facilitates drill performance. Bentonite also absorbs organic and inorganic materials from a mixture of water and helps to absorb and increase the viscosity of drilling waste. Common bentonites that using in drilling mud are:
- Bentonite with standard Ecma
- Bentonite with standard Ecma API
Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate is found in the form of limestone or calcite in white to grainy in nature. Properties such as reasonable prices, low oil absorption, low hardness, high spread and brightness have led to the use of calcium carbonate as the most common filler in various industries.
In the oil industry, calcium carbonate is added to the drilling fluid as a plutonium-forming agent. It is also used as a weighting agent that increases the density of drilling fluids. Calcium carbonate is used to increase mud density to about 1.44 kg/m3, and is preferable to barite because it is acid-soluble and can be dissolved with hydrochloric acid to clean up production zones. Other applications of Calcium carbonate are:
- Construction industry
- Road industry
- Paint industry
- Plastic industry
- Adhesive and Resin industry
The most important characteristics of Calcium Carbonate are shown in following table:
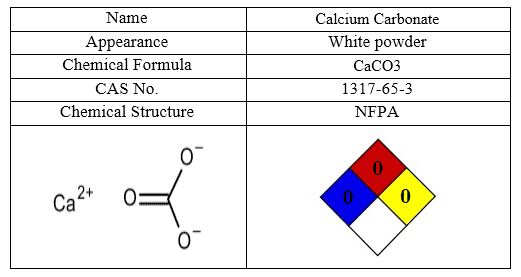
Calcium Nitrate
Calcium Nitrate consists of nitrate nitrogen and calcium ion. Calcium Nitrate is one of the high-Calcium salts that is white and because of its high solubility in water, it has many uses in contrast to other commonly used calcium compounds. The most important use of calcium nitrate is agricultural manure.
For the production of this substance, the acidification method utilizes Calcium Carbonate or limestone with nitric acid, and then it is neutralized by ammonia. Calcium Nitrate is used in two ways as a coagulating agent and also as a salt in drilling mud. Other applications of Calcium Chloride are:
- Melting salts for heat transfer and storage
- Wastewater treatment
- Latex production
- Concrete production
The most important characteristics of Calcium Nitrate are shown in following table:

Carboxy Methyl Cellulose
Carboxy Methyl Cellulose (CMC) was first produced in Germany and then in the Americas and other Western countries in two industrial and food grades. CMC is used as a viscosity modifier or thickener, and to stabilize emulsions in various products including ice cream.
CMC is known for its excellent water retaining capacity. CMC is an anionic polymer in water that is made from cellulose and acts as a major factor in improving the quality of flowering drilling in two ways. The type with high viscosity of this material is used to create a concentration and its low viscosity is used to reduce the amount of drilling waste. Among other uses of this article are the following:
- Water absorbent and preservative
- Drilling wells
- Food industry
- Cosmetics
- Paint and Resin Industries
- Detergents and soaps
- Toxins and pesticides
The most important characteristics of the CMC are shown in following table:
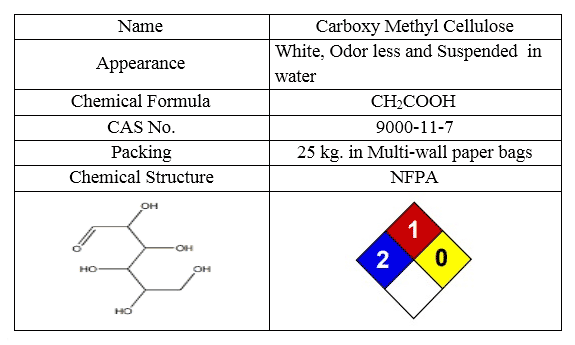
Cross Linker
Cross-linkers compound are typically a metallic salt, mixed with a base-gel fluid, such as a guar-gel system, to create a viscous gel used in some stimulation or pipeline cleaning treatments. When a cross-linker added to the gel, a complicated compound is formed, viscosity and operation condition has improved.
Using cross-linkers reduces the use of extra additives that using to control the viscosity. This property will remain as long as a distracting agent is added to the gel. Other applications of Cross-linkers are:
- pipeline cleaning treatments
- Increasing the hydraulic performance of drilling gels
- Increase the speed of drilling wells
Defoamer
A defoamer or an anti-foaming agent is a chemical additive that reduces and hinders the formation of foam in industrial process liquids. Foam during the transfer process, creates many problems for oil and refinement production. Various physical and chemical methods can be used to control foam formation, including ultra-sonication and thermal fluctuation. Presence foam caused the following problems:
- Excessive deposition during the process
- Delay and stop in the process
- Cavitation in the pumps
- Reduced efficiency of equipment
- Increased maintenance costs
- Increase process time
Therefore, it can be said that the presence of the foam leads to a reduction in productivity and income. Anti-foaming agents are additives that, by reducing the surface tension and thus releasing trapped gas in the liquid. The most famous anti-foaming agents that are widely used to solve these problems include silicon, actinic alcohols, various glycols, aluminum stearates and sulfone hydrocarbons. Antifouling application in the oil industry can be divided into two parts:
- Oil and gas production: drilling mud, oil and gas separation, gas refinery and gas dehydration
- Refinery processes: vacuum distillation, cracking process, crude distillation, benzene-toluene-xylene extraction, aromatic compounds extraction
Foam Agent
A chemical which facilitates the process of forming foam and enables it with the ability to support its integrity by giving strength to each single bubble of foam is known as foaming agent. It may categorize in two parts including Protein and Synthetic.
One of the methods of drilling that is nowadays in the country has a special priority over other methods of foam. The main reason for choosing this type of fluid is due to advantages such as increasing the drilling speed, reducing final costs and minimizing the waste of drilling mud compared to other fluids. In general, there are two types of foam drilling as following:
- Stable foam or based-blue foam
- compact foam
On the stable foam, the liquid phase can include surfactants, salts or corrosion inhibitors, none of which has a significant effect on the fluid phase viscosity. But on the compact foam the liquid phase, in addition to the material mentioned, includes polymers, such as viscosifiers. Foaming agents that are added to drilling fluids, should initially have a good stability against solids and hard liquids, high salinity and temperature. Among other uses of this article are the following:
- Liquid transfer for concentrated gas
- Sustainability of oil and gas wells
- Additives using for acidic properties treating
Gelling Agent
The gelling agent is used as stabilizer, emulsifier and also viscosity enhancer for drilling oil and gas wells. Among the gelling agent can mention the agar.
Special characteristics of this material have been considered to be gel agents. The agar is insoluble in cold water and soluble in hot water, it is also the strongest known gel maker, and even forms a gel at a concentration of 0.04% and at temperatures higher than the thermal temperature of the gel can form a gel. For example, the gel forms at 30-40℃, but the gel stable to 80-90℃. This gelling agent, a non-branching polysaccharide derived from the red alga cell wall, is mainly derived from Gelidium and Gracilaria. Other applications of gelling agent are:
- Oil and Gas Industries: As a Stabilizer and Emulsifier
- Chocolates: As Topping
- Microbiology: in the production of various culture environments
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetic, sanitary: as a gel
H2S Scavenger
The process of removing H2S is known as gas sweetening, by either iron sponge H2S scrubbers or chemical scavengers. Typical H2S scavengers used in the oilfield are amine based chemicals. Hydrogen is a highly toxic gas sulfide that is unwanted in the process of decomposition of organic matter and crop.
H2S gas, in addition to severe corrosion in process equipment, is highly toxic and causes serious poisoning for humans and animals. The process of removing H2S gas, which is the most important gas sweetening process, can be carried out in two ways: iron sulfide or chemical film formation. Chemically based chemicals with a disintegrating H2S amine are common in the oil industry, which are divided into two groups:
- H2S Regenerative Decontamination: Monoethanolamine, Diethanolamine, n-methyl-diethanolamine, Diisopropylamine and Diglycoleamine
- Non-reducing detoxification H2S: Triazine, aldehydes, metal carboxylate and chalcids
The efficiency and method selection in a H2S removal process is a function of the amount of initial gas available in the primary system. When the H2S level is less than 500 ppm, the use of adsorbent is the most economical choice and at a level higher than 500 ppm should be used in other ways.
Iron Control Agent
Precipitation of iron compounds can cause damage to the reservoir permeability or exacerbate sludging issues causing formation damage. Control of the iron with iron control agents is essential to ensure the prevention of formation damage. Two classes of iron control agents are reducing agents and chelates.
- Iron reducing agent
- Iron complex agent
The common feature of iron control agents is to stabilize iron ions in the process. The iron control agent is used to reduce the iron ions contained in acidic solutions. One of the applications of these materials is their use in the process of digestion acidification. The iron control agent consists of a mixture of sulfur dioxide, sulfuric acid, sulfite salts, and iodine-containing material. The iron control agent may also contain low levels of 2-morpoventanol and thioglycolic acid, or other salts
PAC
Poly aluminium chloride (aluminium chlorohydrate) also simply called PAC, is used in deodorants and as a coagulant in water purification.
The process of coagulation in the wastewater treatment industry has a special place. The mechanism of performance of old coagulants is based on instability, which is done by compressing a double electric layer around the colloidal particle. Aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride are the most common primary coagulant to remove impurities and water contaminants. In recent years, poly aluminum chloride has been widely used to replace former coagulants.
Poly aluminum chloride performs instability through adsorption at the surface of the colloidal particle and creates particle-polymer-particle bonding bridges. This mechanism increases the rate of particle instability, resulting in the rapid growth of particles and improved separation. Among other uses of this article are the following:
- Drinking water
- Industrial waste water treatment
- Urban wastewater treatment
- Purification of agricultural waste water
- Using in paper industry
- Using in textile and leather industries
The most important characteristics of the PAC are shown in following table:

Potassium Silicate
Potassium Silicate is a mineral compound that is most important in the production of chemical fertilizers. The presence of two elements of silica and potassium together, in addition to exacerbating the effect of each other, also increase photosynthesis. Potassium silicate in drilling fluids is used as a buffer solution to keep pH below 11. Other applications of Potassium Silicate are:
- Soap industries
- Industrial Cleaners
- Adhesive industry
- Peroxide stabilization and corrosion control
The most important characteristics of Potassium Silicate are shown in following table:
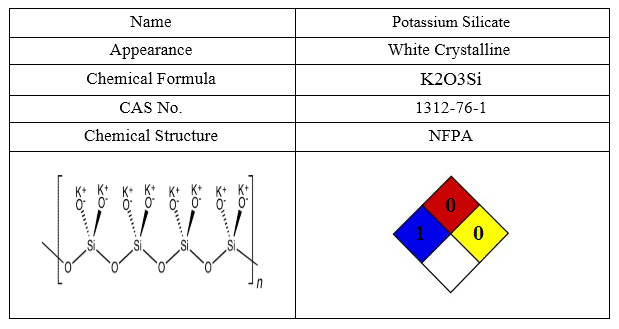
Soda Ash
Soda Ash is the common name for unhydrated of sodium carbonate with industrial application. Nicholas Lebens In 1791, produced sodium carbonate in the present form, and by the nineteenth century the product was mainly extracted from the ashes of plants. Sodium carbonate is also naturally occurring in nature and produced by various chemical methods. The most important application of sodium carbonate in glass production. Sodium carbonate is used in water-based drilling fluids to reduce the calcium hardness. When drilling fluid contains a lot of anhydrite, it is necessary to use a polymer that does not react with calcium. Other applications of Soda Ash are:
- Glass Manufacturing Industries
- Bricks Industries
- Food industry
- Additive in urban reservoirs to neutralize the acid chloride effect
The most important characteristics of Soda Ash are shown in following table:

Sodium Sulfite
Sodium Sulfite is a sodium salt solution of sulfur acid. Industrial Sodium Sulfur is made by reacting sulfur dioxide with a solution of sodium carbonate and the primary compound generates sodium bisulfite, which is converted to sulfite by reaction with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. Sodium sulfite is mainly used in the paper industry. In drilling, Sodium Sulfite is an oxygen scavenger used to impart better temperature stability to the added polymers. At higher temperatures 75℃, polymers will begin to degrade (oxidize) by treating out dissolved oxygen there is better longevity. Other applications of Sodium Sulfite are:
- Water Treatment Industries
- Photography industry
- Textile Industry
- Military industries
The most important characteristics of Sodium Sulfite are shown in following table:
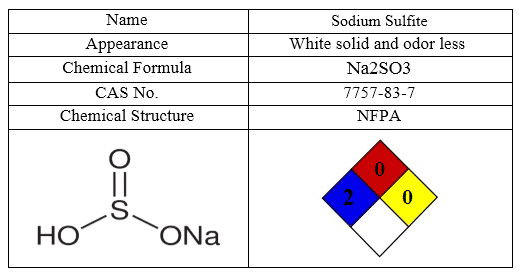
Xanthan Gum
Xanthan gum is a natural biopolymer produced by fermentation of sugar, dextrose, corn syrup or starch by Xanthomonas campestris. Xanthan gum is used as a stabilizer in many applications to provide excellent particulate suspension, emulsion stability, viscosity, moisture retention, and freeze-thaw stability.
Xanthan gum is a biopolymer discovered in the US Department of Agriculture’s Department of Applied Research and Development in 1950.
Xanthan Gum is the first and most important bacterial heteropolysaccharide. Due to the presence of acetyle and pyrolyl groups, xanthan gum is known as an ionic polysaccharide. In order to make commercial Xanthan gum, Zanthomonas Campest bacteria is added to a liquid solution containing plant material such as corn, soybeans or wheat, fermentation occurs naturally and bacteria produce as a byproduct of xanthan gum.
The resistance of this gum has made it a reliable alternative, including stimulant control agents. This gum is a drill mud additive that is more efficient and environmentally friendly than other additives. The main application of xanthan gum is as a thickening agent that increases viscosity. Other uses of this substance are the following:
- Uses as viscosifier because of its rheological properties
- Sanitary and cosmetic industries
- Pharmaceutical Industries
- Agriculture
- Road construction and mining
Barite
Barite The natural compound of barium sulfate is BaSO4, Barite is a dense sulfate mineral that can occur in a variety of rocks, including limestone and sandstone, with a range of accessory minerals, such as quartz, chert, dolomite, calcite, siderite and metal sulfides. Barite is commonly used to add weight to drilling fluid. Barite is of significance to petrophysicists because excess barite can require a correction factor in some well log measurements.Barite is in the normal expression white to light gray but may also be seen in other colors. The most important uses of barite, are:
- Oil and gas drilling: Used in deep drilling for oil and gas as an agent to prevent material leakage and control of well pressure. The use of barite due to high specific gravity, simplicity of use during work, chemical neutrality, softness and reasonable prices are used in drilling mud. The amount of barite consumed per km of drilling is reported to be about 430 tonnes.
- Production of Barium-based Chemicals: Barite is used as a feedstock in the production of barium sulfate, chlorobium and barium oxides.
- Glass industry: Barite is used as a melting agent, bubble reduction, product luminosity and transparency.
- Filler agent: Barite is used in paints, plastics, paper and rubber as filler material.
Buffering Agent
Buffer or tampons are solutions that their pH does not change due to the addition of a small amount of acid or bases. Buffering system that resists a change in pH. It comprises three components: water, weak acid (or weak base) and salt of the weak acid (or salt of weak base).
In a buffered system, the concentration of H+ and OH- ions remain relatively constant because they are in equilibrium with one or more of the other two components, even with the addition of acids or bases. These solutions are very important for chemical and biological systems. MgO is used to buffer the pH of a drilling fluid at 10. At a pH below 10 this product will dissolve and bring the pH back up to 10. The additive must be mixed in excess for the buffering to take place.
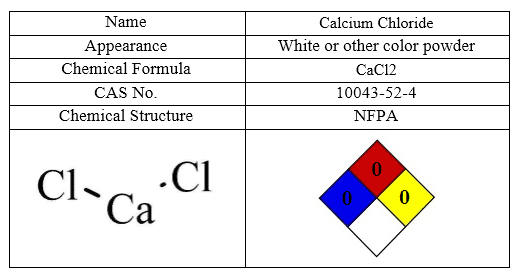
Calcium Chloride
Calcium Chloride is a salt of calcium and chlorine, which acts as an ionized halide sample and solid at room temperature. Calcium chloride has a relatively high solubility in water and the solubility of this substance in water increases with increasing temperature. Calcium Chloride can act as a source of Calcium ions in the solution, this property can be useful for the displacement of ions from the solution. Calcium Chloride is one of the most important and practical mineral chemicals used in drilling industry as a drilling mud. Calcium Chloride used to make drilling and workover fluids or brines with a density about 1.39 g/cm3 at saturation. Other applications of Calcium Chloride are:
- Cooling industry
- Water adsorption
- Pigments production
- Glycerol production
The most important characteristics of Calcium Chloride are shown in following table:
Clay Stabilizer
Migration or swelling have always been one of the problems of geotechnical engineering due to the inability to heavy loads. Therefore, research has always been done to improve their properties, such as increased resistance, reduced permeability, increased load capacity and increased stability. One of the methods for increasing the strength of the layers of the earth is to fix these layers with different materials. Clay Stabilizer is a chemical additive used in stimulation treatments to prevent the migration or swelling of clay particles in reaction to water-base fluid. Clay stabilizers act to retain the clay platelets in position by controlling the charge and electrolytic characteristics of the treatment fluid.
Corrosion Inhibitors
A corrosion inhibitor is a substance when added in a small concentration to an environment, reduces the corrosion rate of a metal exposed to that environment. Inhibitors often play an important role in the oil extraction and processing industries where they have always been considered to be the first line of defence against corrosion. Corrosion inhibitors, prevent damage to materials and equipment, create a thin layer of protective membranes on the surface of the material. The first Studies about Corrosion Inhibitors focused only on the hydrophilic phase, but new researches focused on the effectiveness of corrosion inhibitors in the crude oil phase.
Although corrosion inhibitors are categorized into two groups including organic and inorganic compounds based on the nature of the ingredients, but other categories are proposed for these materials. For example, based on the performance mechanism, corrosion inhibitors are categorized into three cathodic, anodic and cathodic-anodic mixtures. Based on the system used, corrosion inhibitors were divided into three groups including water-soluble, oil-soluble, and three-phase corrosion inhibitors. The most important factor in the performance of corrosion inhibitors is the pH of the environment. Keeping pH in a constant amount in various gas systems by using of glycol, is a mechanism that is used in Iran to prevent corrosion.
DE-EMULSIFIER
A large amount of petroleum which is produced from petroleum-bearing formations is contaminated by water or aqueous solutions of sodium chloride or other salts in emulsified form. Such water containing systems occur predominantly in the form of water-in-oil emulsions. The presence of water in crude oils causes several problems such as increasing of viscosity, corrosion of pipeline, unusable waste products, and also making problems for storage. With using of De-emulsification can decompose water-crude oil emulsion or destabilize it. Thus two immiscible phases will produce, so separation of water from crude oil makes easier. In general, three types of emulsions can be considered for crude oil-water emulsion:
- Emulsion of oil in water
- Emulsion of water in oil
- Multiple emulsions
The mechanism of De-emulsifiers replace some of surfactant and decrease the surface tension of water-oil interface. Among of the De-emulsifier that are proposed for use include sulfanates, polyglycol ether, phenol oxylates, and naltyl phenol acetoxide derivatives. The most important factors affecting on the performance of a De-emulsifier are:
- viscosity of Initial crude oil
- Type of De-emulsifier
- Stability of oil-water emulsion
- Emulsion concentration
- Amount of used De-emulsifier
- Amount of salt in the water
- Temperature
- Freshwater rate injected into process oil
Drilling Detergent
Drilling mud plays an important role in drilling wells so that it creates the necessary hydrostatic pressure to prevent the flow of fluids into the well. Drilling mud discovery is a mixture of a variety of emulsifiers, which makes the powder and additive material distributed in a water-based drilling fluid in a uniform and stable manner. Also, drilling detergents enhance the porosity of powder additives and prevent clay particles from sticking to metal equipment and internal wall space. One of the most important features of this material is accelerating and facilitating the separation of materials extracted from the wells left from drilling mud at the outlet of the well.
Friction Reducer
Friction-reducing agent alters fluid rheological properties to reduce friction created within the fluid as it flows through small-diameter tubulars or similar restrictions. Using friction reducing agents, the fluid friction value can be reduced to 60%, so the injection speed will increase with the use of these materials. Among the materials that used as friction reducing agents, polymers based on polyacrylamide can be mentioned.
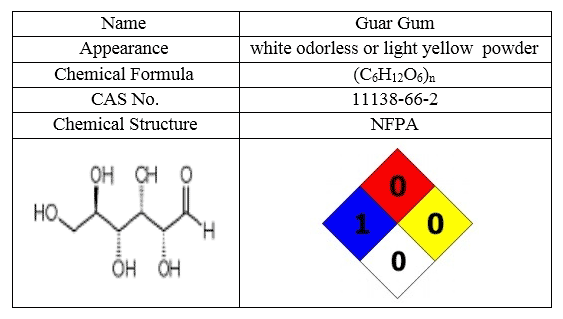
Guar Gum
Guar planting started for the first time in India, and then the high resistance to this plant in difficult atmospheric conditions led to the massive use of Texas and Oklahoma in 1903 for commercial exploitation.
Gum is derived from guar seeds or cyamopsis tetragonoloba termed as Guar Gum. Guar Gum can also be termed as guaran. These seeds have high low-shear viscosity as evaluated with other hydrocolloids like.
Guar Gum Powder is a water-soluble polysaccharide that is stable against heat. To increase the production of oil and gas, oil drilling is widely used in guar gum. Guar gum makes a better colloid in the drilling mud well. As a result, the waste water decreases and the viscosity of the solution is set and the properties of the flow of drilling mud are stabilized and adjusted. Guar gum is also used in the hydraulic fracture process in the production of crude oil and in the digging of oil wells. Among the other uses of Guar Gum, one can mention the following:
- Food industry
- pharmaceutical Industries
- As a Suspension Agent
- Increase the balance and viscosity of drilling mud
The most important characteristics of the Guar Gum are shown in following table:
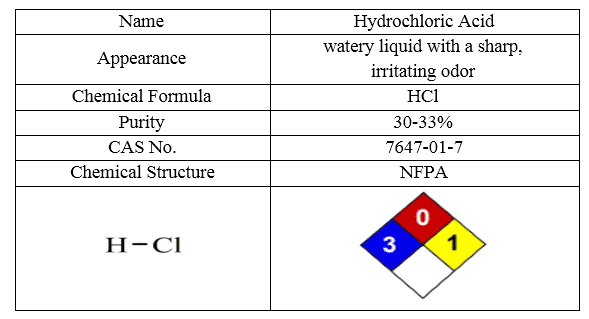
HCl
The conventional acid treatment of wells uses the hydrochloric acid (HCl) for conventional Enhanced Oil treatment of hydrocarbon wells. Hydrochloric acid was first detected by Jabber Hai, a major Iranian alchemist in the process of H2SO4 and NaCl reaction. Hydrochloric acid is a highly corrosive mineral acid, and it is a basic chemical substance that is widely used in the industry.
One of the common ways of increasing the removal of oil and gas damage reservoirs is to stimulate wells by injection of acid to increase the permeability of the reservoir rock. During extraction operations, the accumulation of particles in the organic phase-water phase interface and the formation of stable emulsions in the wells can reduce harvesting. In these cases, it can be prevented by stimulating the well with hydrochloric acid. Among other uses of hydrochloric acid are:
- Cleaning of metals
- Detergents
- Production of organic and inorganic compounds
- pH control and neutralization
- Ion resuscitation
- Preparation of ethylene dichloride
The most important characteristics of the HCl are shown in following table:
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide, also known in the industry as Magnesium or Pericles, is the most important industrial magnesium compound used in many industries. Magnesium oxide is a mineral that is made from carbonate mineral gems. After extraction in the calcination furnace, carbonate rocks are oxidized after carbon dioxide separation and converted to a soft powder using a mill. MgO is used to buffer the pH of a drilling fluid at 10. At a pH below 10 this product will dissolve and bring the pH back up to 10. The additive must be mixed in excess for the buffering to take place. Other applications of Magnesium Oxide are:
- Steel industry in electric arc furnaces
- Cement industries
- In Non-Ferrous Steel Industries
- Glass Manufacturing Industries
The most important characteristics of Magnesium oxide are shown in following table:

KCl
Potassium chloride is Viscosifier and Filtration control agent for water based Mud Systems. It is used in drilling muds for controlling borehole stability.
It is used to increase the density of any mud system while maintaining rheological properties
It is utilized in drilling muds to extract drill cuttings from the bit. Potassium chloride is a salt that consists of a combination of potassium and chlorine halogen.
One of the common chemicals in the oil well drilling industry is potassium chloride solution, which is used for reasons such as low cost and easy access, compatibility with drilling fluid additives, loosely stabilized and water-sensitive clay, and the rapid dissolution of its use is very common. Among other uses of potassium chloride, the following can be mentioned:
- Agriculture industry
- Waste industries
- Chemical colors
- Pharmaceutical Industries
- Glass industry
- Ceramic and tile industry
- Food industry
The most important characteristics of the KCl are shown in following table:

SDVES
SDVES is a mixture of cationic and chloric acid surfactants, along with a kind of macromolecular structure of Maisel. Which is added to the drilling fluid as a gel agent. SDVES can be added continuously to the fluid before pumping or during pumping. However, it is recommended to be added to the fluid before pumping into suitable mixing. Other applications of SDVES are:
- High performance as surfactant
- Proper performance in a wide range of pH
- Clear appearance and proper solubility in water
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate or baking soda is one of sodium salts in combination with carbonic acid, that one of acid hydroxide compound replace with sodium. Sodium Bicarbonate is used in drilling to remove impurities from calcium remaining in cement. One of the advantages of using sodium Bicarbonate compare with soda ash is lower pH of Sodium Bicarbonate, which helps reduce the pH of the cement. Other applications of Sodium bicarbonate are:
- Cosmetic industry
- Food industry
- Textile Industry
- Rubber and plastic industries
The most important characteristics of Sodium Bicarbonate are shown in following table:

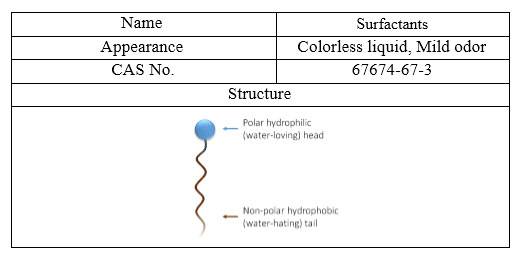
Surfactants
Surfactants are organic compounds that are amphiphilic that lower the interfacial tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or between a liquid and a solid.
Surfactants are organic compounds made up of a hydrophobic head (water repellent) and a hydrophilic head (water absorber). Therefore, they are soluble in either organic solvent or water and reduce surface tension in the oil-water interface, depending on the structure of their molecules. In fact, surfactants, due to their two-personality of their molecular structures, can greatly alter superficial energy levels. This feature makes it a lot of applications. Surfactants can be divided into four main groups:
- Anionic: With one or more negative charges, using in detergents
- Cationic: with one or more positive charges, application in bactericide production, dressing emulsions and emulsifiers
- Amphoter: has both cationic and anionic groups, using in shampoos and skin cleansers production
- Non-ionic: No charge, using in detergents
The most important characteristics of the Surfactants are shown in following table:
Xylene
Xylene is a mixture of fat and a colorless liquid, and is often considered as solvent in chemical reactions. Xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon molecule containing a benzene ring with two methyl side chains. Xylene has three isomeric forms: iso-isomer, meta and para with various physical and chemical properties. Xylene is used as a solvent and emulsion breaker in workover operations to clean up reservoirs.
About 0.5% to 1% percent of the crude oil is xylene and found lower than 1% in gasoline and jet fuel. Xylene is used to remove of asphaltene compounds, asphaltenes of crude oil, which are unsoluble in normal alkenes and dissolved in toluene. Asphaltene blocks the production wells and reduces the refining speed and, in the worst case, causes a complete stop extraction process. Other applications of Sodium Sulfite are:
- Production of synthetic fiber raw material
- pharmaceutical Industries
- Insecticides
The most important characteristics of Xylene are shown in following table:


