
Materials List – Mine
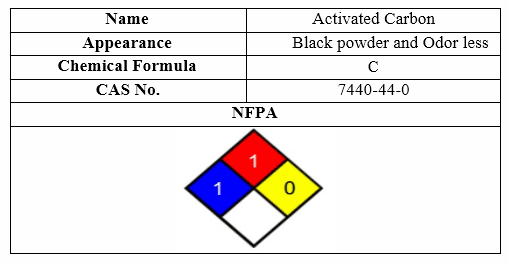
Activated Carbon
Adsorption is the attachment or adhesion of atoms, ions and molecules from a gaseous, liquid or solution medium onto the surface of an adsorbent. Activated carbon is a highly porous adsorptive that has a complex structure composed primarily of carbon atoms. Activated Carbon is the best choice for purifying raw materials, intermediaries, and products in the oil and gas industry and also sweetening processes, catalytic de-chlorination, or gas cleaning scrubbers to increase their.
Activated carbon for high surface area, porosity and the ability to absorb gases and chemical fluids known as an absorbent. By using the adsorption process can remove dyes, heavy metals, hydrocarbon component from wastewater, thereby increase the system resistance versus organic loading. Granular active carbon has an important role in purifying the scrubbing liquids and increase process efficiency by affecting factors such as Amine Foam, corrosion. Some of other activated carbon application example are:
- Remove chlorine from water
- Construction of catalysts
- Biomass carrier
- Carrier of chemicals
The most important characteristics of the Activated Carbon are shown in following table:
Flocculant
Flocculation and Coagulation treatment chemicals are used in effluent water treatment processes for solids removal, water clarification, lime softening, and sludge thickening. Impurities in groundwater and surface water include dissolved particles and suspensions. The chlorine ponds are used to separate these substances from the water. Clarifiers are tanks made with mechanical tools that are used for continuous removal of precipitated particles resulting from filtration. Coagulants and flocculants are used in these ponds.
Polyacrylamide flocculant or polycarbonate is a chemical substance that accelerates the process of separating solid particles from the liquid and facilitates the process of purifying the wastewater and obtaining clear water. Suspensions differ from source, charge, particle size, shape, and density. The correct use of coagulant and flocculant agents is dependent on the correct knowledge of suspended particle specification. Flocculants are used not only in the water purification industry, but also in the solid-liquid separation industry, including the processes of deposition, water treatment, condensation and dehydration, including:
- Mining industry: use in the processing of mining and construction gems drilling and mining
- Paper industry: Use as a fiber reinforcement and drying agent
- Paint and leather industry: Use as a sedimentation agent
- Agricultural industry: Use as a soil stabilizer to prevent erosion
Sodium Cyanide
Sodium Cyanide was first produced in 1834 by Bradarran Rogers. They heat the color combination containing two-capacity iron trivalent iron derivatives and sodium carbonate and after cooling the mixture, the sodium cyanide was extracted with alcohol. By 1899, half of the cyanide produced in Europe was produced by the blast process, and from the beginning of the 20th century another method, called Process Cisner, was used to make sodium cyanide.
Cyanide is a chemical process for the recovery of gold and metals that are scattered very tiny in ore. The cyanide process is also used to recover sulfide-coated gold. The ore or waste is added to the cyanide solution, which helps to produce oxygen in order to dissolve the gold in the form of Na [Au (CN) 2]. The amount of sodium cyanide used in this process is 1 to 2.5 kilograms per ton of ore.
In addition to the extensive use of sodium cyanide in mines, this material is used in the electroplating industry as well as in the production of certain chemicals.
The most important characteristics of the NaCN are shown in following table:

